Nice Guidelines Refeeding Syndrome
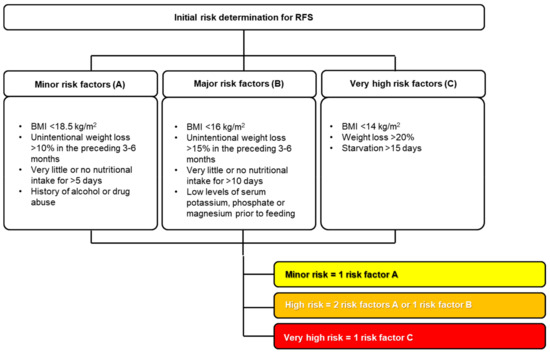
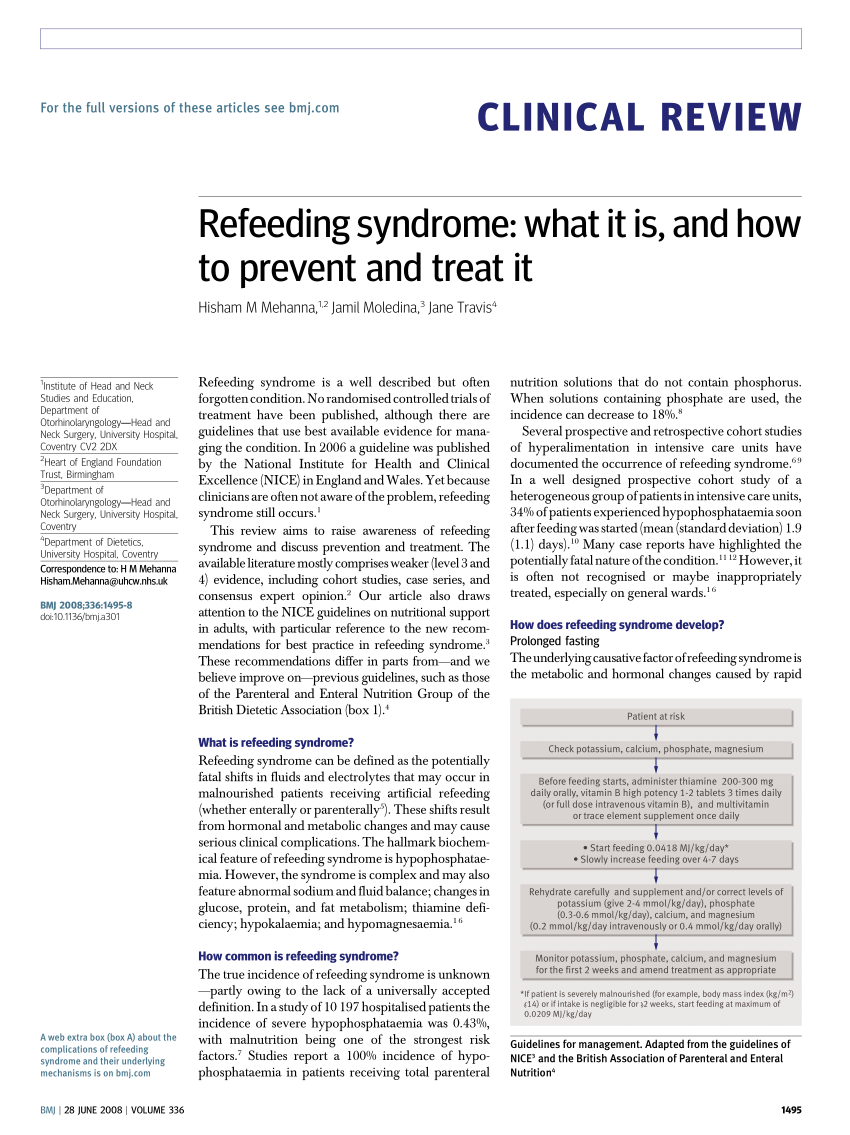
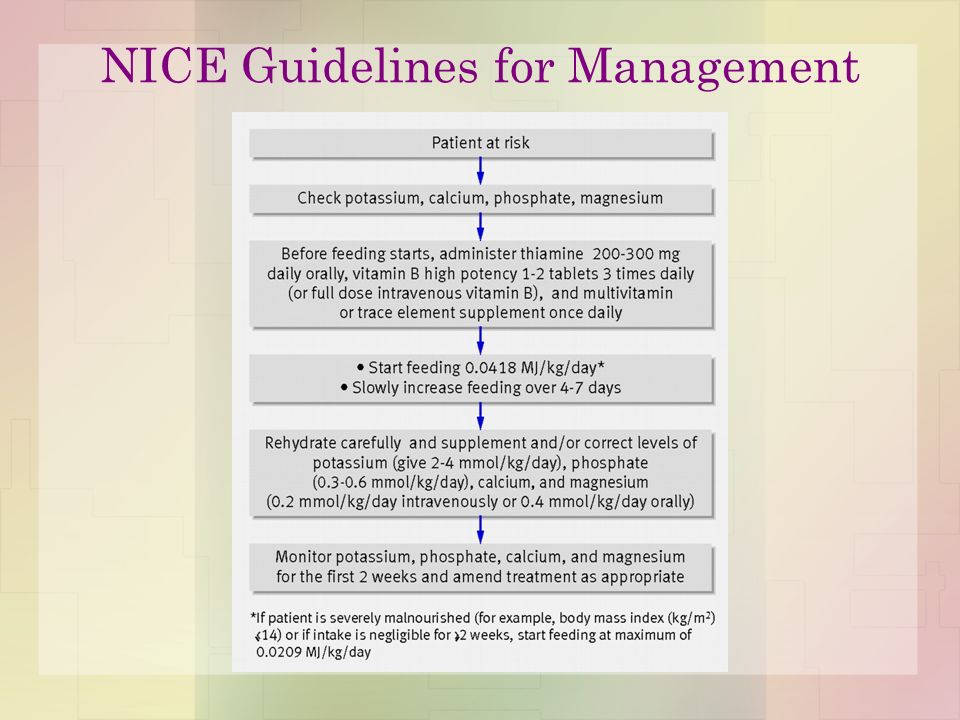
Nice guidelines refeeding syndrome. Carefully restore circulatory volume and monitor fluid balance pulse rate blood pressure and clinical status 4. Some of the common nice National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence UK guidelines refeeding syndrome includes NICE clinical guideline 32 2006 which tells us that you can identify a person with refeeding syndrome by. In patients who are very malnourished body mass index 14 or a negligible intake for two weeks or more the NICE guidelines recommend that refeeding should start at a maximum of 0021 MJkg24 hours with cardiac monitoring owing to the risk of cardiac arrhythmias level D recommendation.
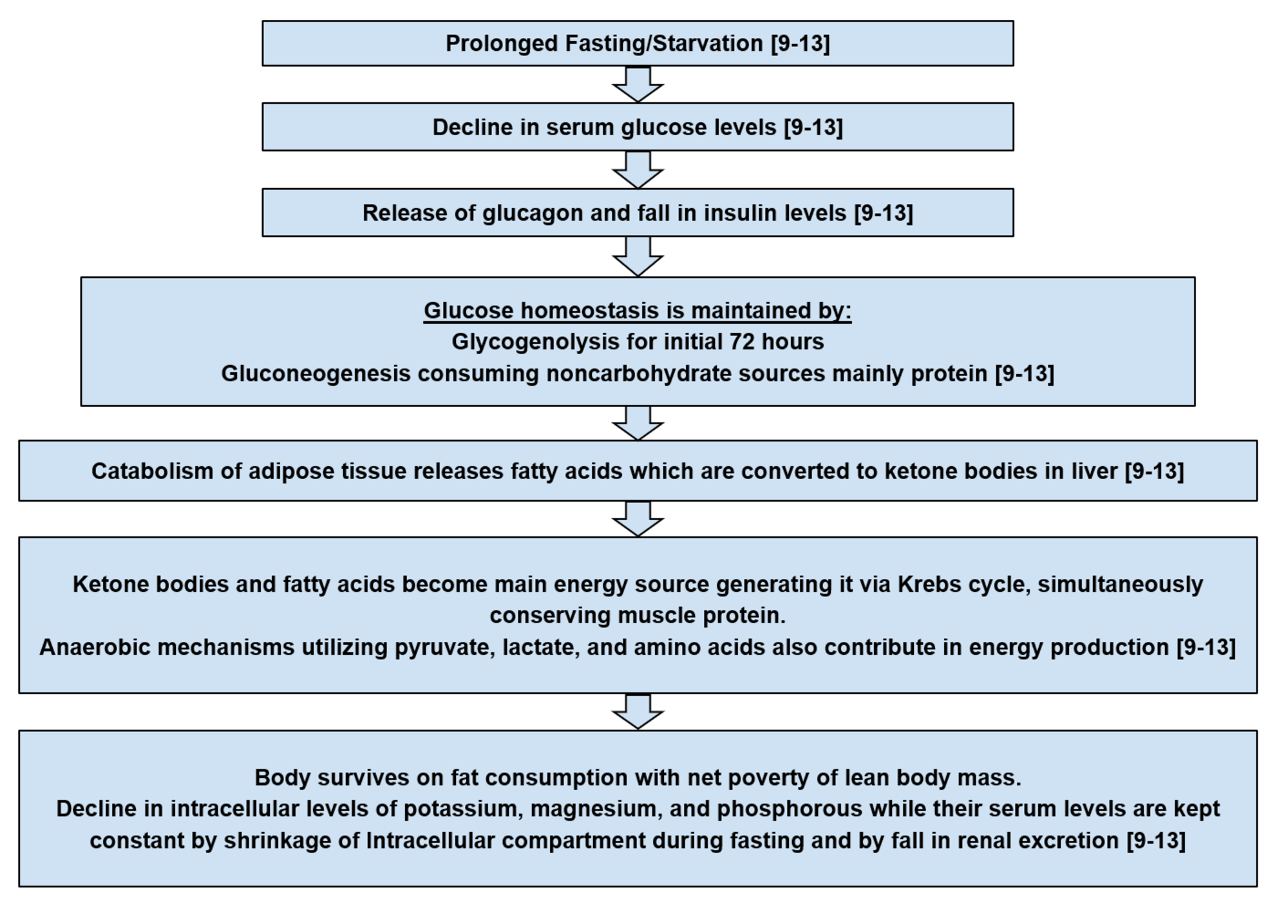
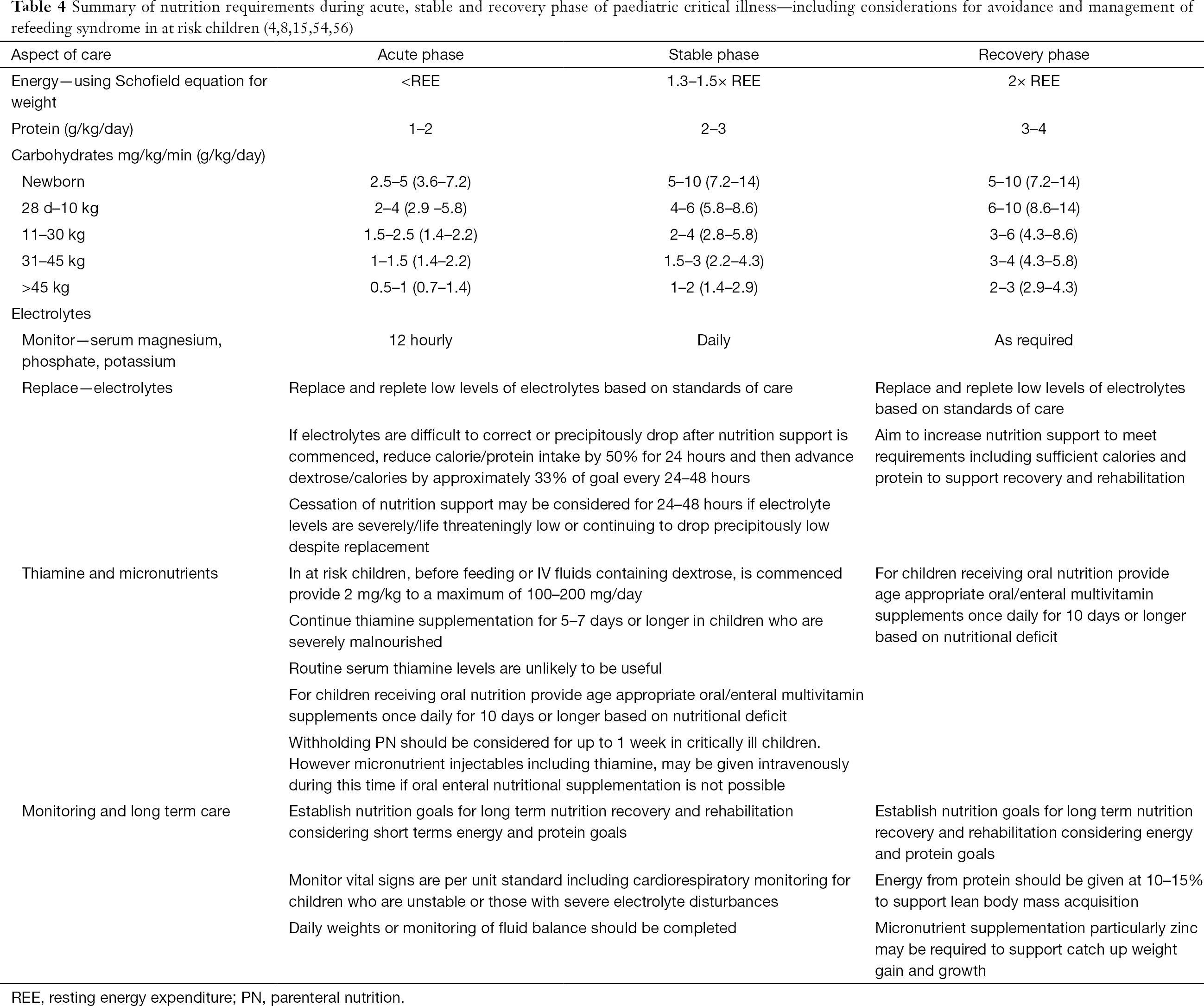
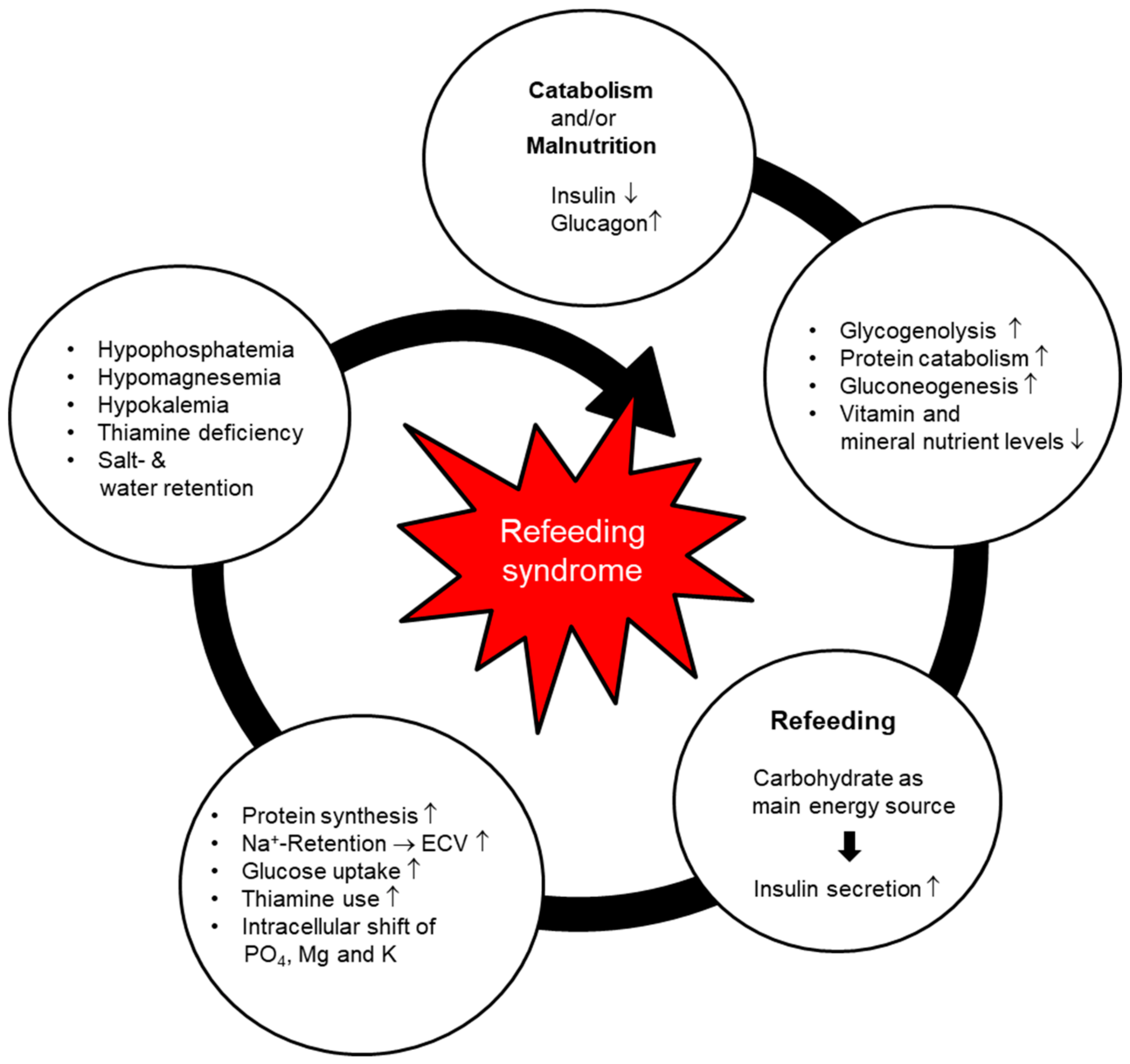
Refeeding Syndrome Definition and Background RS is historically described as a range of metabolic and electrolyte alterations occurring as a result of the reintroduction andor increased provision of calories after a period of decreased or absent caloric intake. Attitudes to NICE guidance on refeeding syndrome BMJ. 2535 kcalkgday total energy including that derived from protein 9 10 0815 g protein 013024 g nitrogenkgday.
In patients who are very malnourished body mass index 14 or a negligible intake for two weeks or more the NICE guidelines recommend that refeeding should start at a maximum of 0021 MJkg24 hours with cardiac monitoring owing to the risk of cardiac arrhythmias level D recommendation3 This explicit specification of the rate of refeeding in severely malnourished. At risk high risk or severe risk. Use of oral supplements 3.
4 SALT assessment Refeeding is potentially a fatal condition defined by severe electrolyte and fluid shifts as a result of a rapid reintroduction of nutrition after a period of inadequate nutritional intake. Patients at high risk of Refeeding Syndrome - Commence nutrition support at a maximum of 10kcalskg body weight. Increase calorie provision only as clinical condition and electrolyte results allow.
Nasogastric feeding Oral intake should be encouraged as the preferred refeeding option. This guideline was previously called nutrition support in adults. Attitudes to NICE guidance on refeeding syndrome.
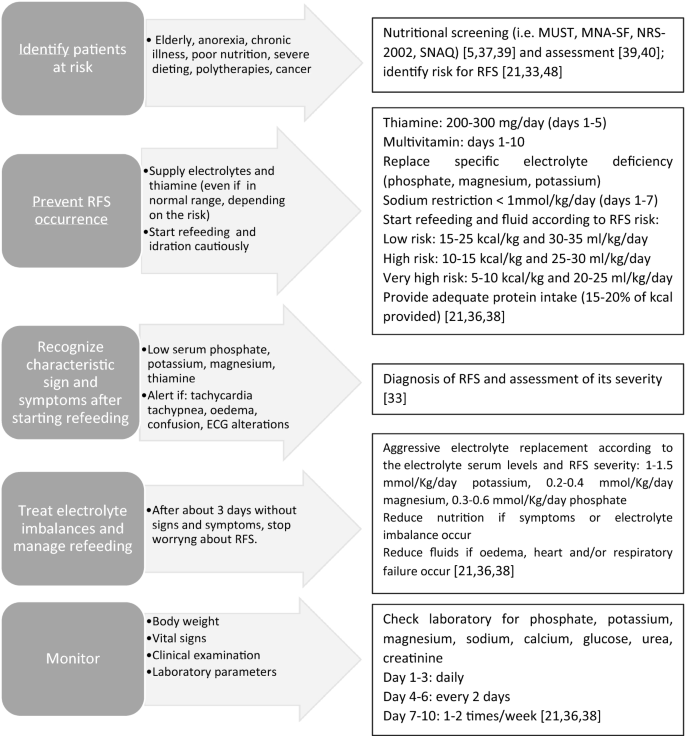
We found no new evidence that affects the recommendations in this guideline. Adult Refeeding Guidelines 9. Identify at risk patients 2.
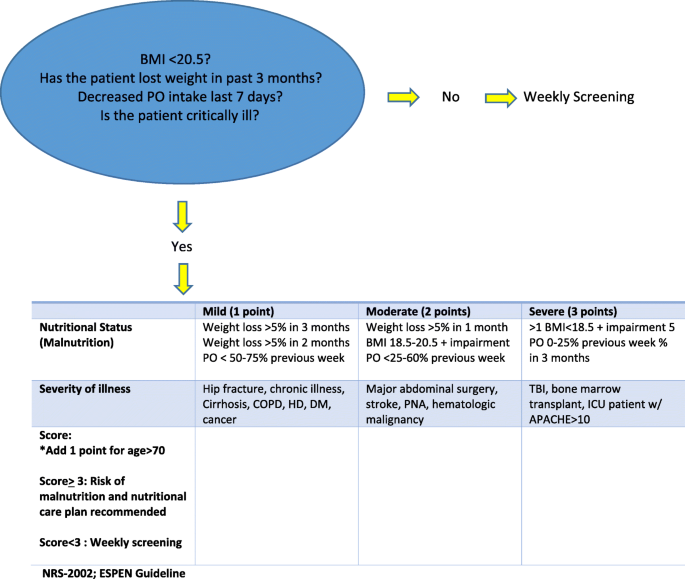
NICE CG32 Refeeding Guidelines. Very little or no food intake for more than 5 days especially if already undernourished BMI 20kgm2 Unintentional weight loss 5 within the last 3-6 months 92.
Oral nutrition support enteral tube feeding and parenteral nutrition.
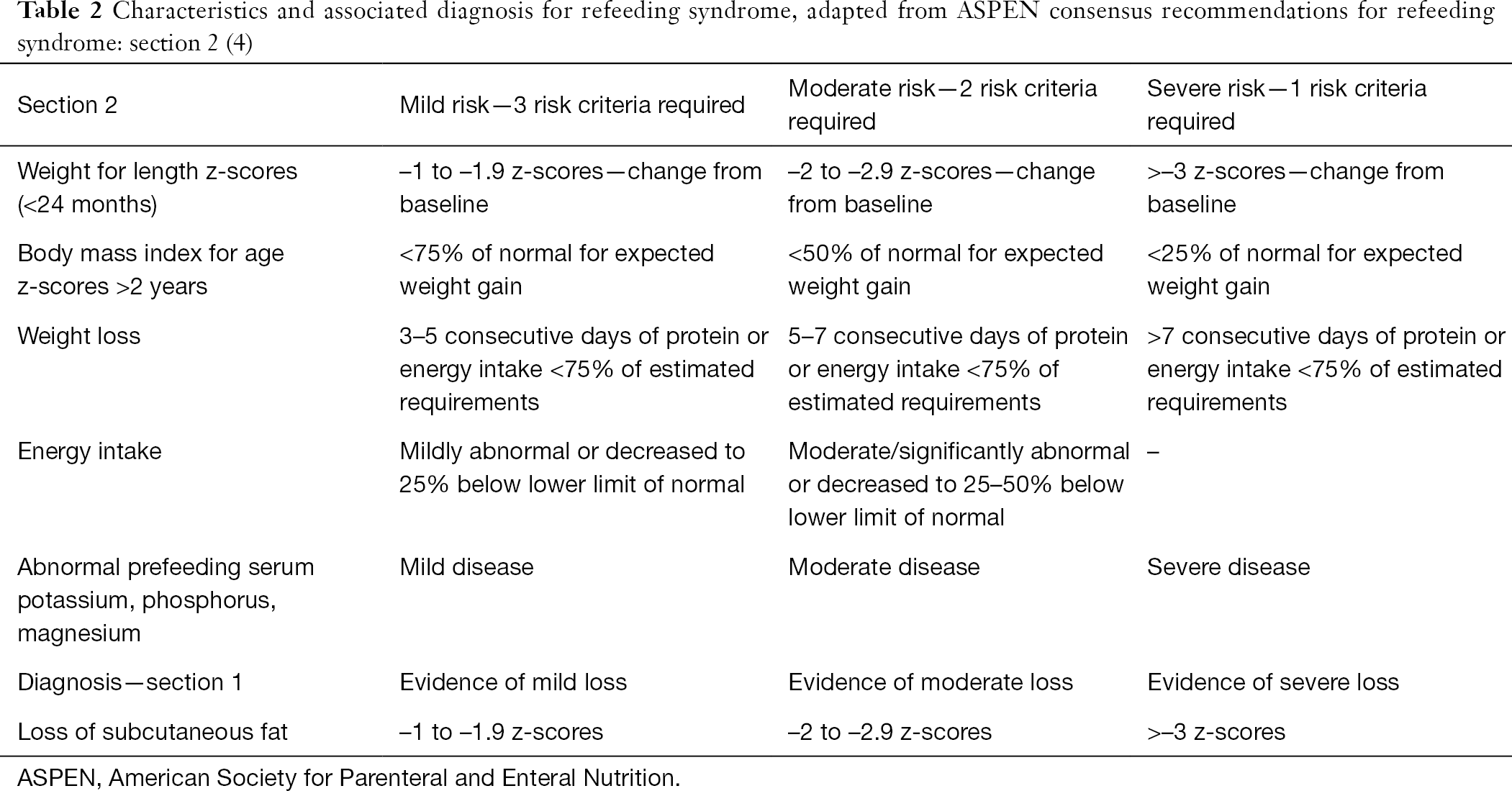
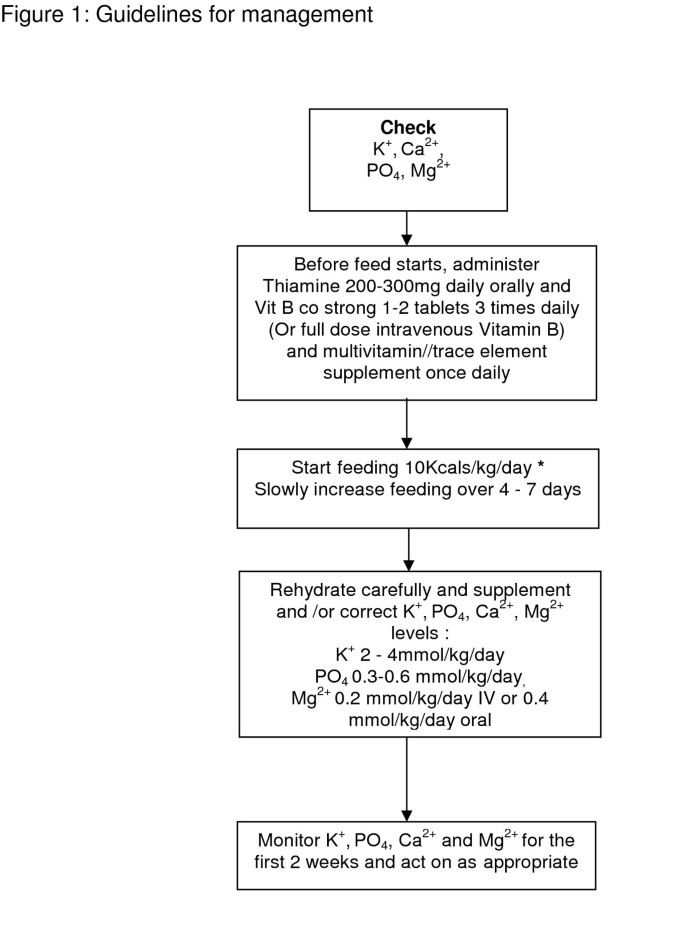
Below 04th BMI centile Recent loss of weight of 1 kg or. Use of oral supplements 3. Carefully restore circulatory volume and monitor fluid balance pulse rate blood pressure and clinical status 4. If the patient is medically unstable however naso-gastric feeding would be preferred. Check and correct electrolyte disturbances 3. What is Refeeding Syndrome. To ensure adequate prevention the NICE guidelines recommend a thorough nutri-tional assessment before refeeding is started3 Recent weightchangeovertimenutritionalcoholintakeand social and psychological problems should all be ascertainedPlasmaelectrolytesespeciallyphosphate sodium potassium and magnesium and glucose. Refeeding Syndrome Guideline Definition. Patients at moderate risk of Refeeding Syndrome Introduce nutrition support at a maximum of 50 of requirements for the first 2 days.
Authors Aminda De Silva Trevor Smith Mike Stroud. Can be categorised as. Attitudes to NICE guidance on refeeding syndrome BMJ. An individual may be at risk and able to recognize refeeding syndrome if any one of the following condition applies. What is Refeeding Syndrome. Is this guideline up to date. Guidelines to avoid the refeeding syndrome 1.





























Post a Comment for "Nice Guidelines Refeeding Syndrome"